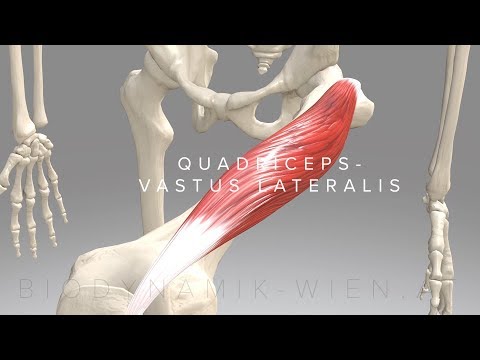
Vastus Lateralis (lateral muscle of the Quadriceps)
The Vastus Lateralis Muscle: Structure, Function, and Significance
Introduction
The vastus lateralis muscle is a prominent and critical component of the quadriceps femoris muscle group located in the anterior compartment of the thigh. As one of the largest muscles in the human body, the vastus lateralis plays a crucial role in lower limb movement and stability. This essay will elucidate the origin, insertion, muscle path, and function of the vastus lateralis muscle, highlighting its significance in human anatomy and biomechanics.
Anatomy of the Vastus Lateralis Muscle
The vastus lateralis is one of the four muscles that make up the quadriceps femoris group, each with a distinct role and function. Understanding the anatomy and function of the vastus lateralis requires exploring its origin, insertion, muscle path, and function.
Origin and Insertion:
Origin: The vastus lateralis muscle originates from the lateral lip of the linea aspera, a ridge on the posterior surface of the femur. It also has origins from the greater trochanter and the intertrochanteric line of the femur.
Insertion: The vastus lateralis inserts into the quadriceps tendon, which then merges with the patella. From the patella, the quadriceps tendon continues as the patellar ligament, attaching to the tibial tuberosity on the anterior surface of the tibia.
Muscle Path:
The vastus lateralis muscle runs along the lateral side of the femur, covering a significant portion of the thigh. It extends from its origin on the femur down to the quadriceps tendon, which provides the attachment to the patella and eventually connects to the tibia.
Function of the Vastus Lateralis Muscle:
The vastus lateralis muscle performs several crucial functions related to lower limb movement and stability:
Knee Extension: The primary function of the vastus lateralis, in conjunction with the other quadriceps muscles, is to extend the knee joint. This action straightens the leg from a bent position and is vital for activities such as standing up, walking, running, and jumping.
Stabilization of the Patella: The vastus lateralis, along with the other quadriceps muscles, helps stabilize the patella (kneecap) during movement. This stabilization is crucial for maintaining proper alignment of the patella within the patellofemoral groove and ensures smooth knee joint function.
Assistance in Hip Flexion: The vastus lateralis assists in flexing the hip joint to some extent, particularly during activities that require rapid and forceful movements, such as kicking a ball.
Significance in Human Anatomy and Biomechanics:
The vastus lateralis muscle is of significant importance in the anatomy and biomechanics of the lower limb. Its function in knee extension and stabilization is crucial for maintaining an upright posture and facilitating various daily activities that involve lower limb movement. Additionally, its attachment to the patella and the subsequent connection to the tibia via the patellar ligament highlights its role in ensuring the efficiency and stability of the knee joint.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the vastus lateralis muscle is a vital muscle of the quadriceps femoris group, playing a crucial role in knee extension and stabilization. Understanding its anatomy and function provides insights into the intricate interplay of muscles in the lower limb, emphasizing the muscle's essential role in facilitating lower limb movement and supporting overall locomotion and physical activities.